Update: This article was last updated on 15th February 2024 to reflect the accuracy and up-to-date information on the page.
Finding the right school for your child can be daunting, especially if you’re on a tight budget or traditional public schools in your area need to meet your expectations.
While public schools are free and offer a diverse curriculum, they may have limitations that don’t suit your child’s unique abilities and interests. Private schools, on the other hand, can provide a more tailored education but come with a hefty price tag that not everyone can afford.
Enter charter schools – publicly funded but independently operated schools that offer a unique blend of innovation and flexibility. In the US, there are approximately 7,000 charter schools to choose from.
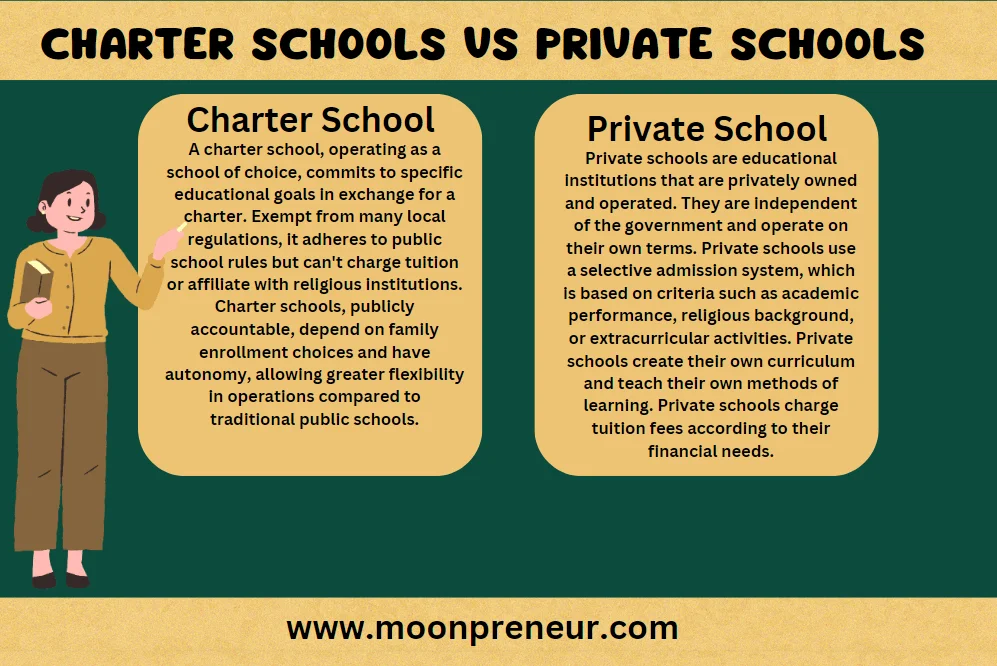
In this article, we’ll help you understand the key differences between charter schools and private schools to help you make an informed choice.
10 Key Differences Between Charter Schools and Private Schools
| Features | Private Schools | Charter Schools |
|---|---|---|
| Funding | Tuition, grants, donations, endowments | Public institutions, non-government organizations, private entities aligned with the school's philosophy |
| Tuition Costs | Yes, usually around $12,350 per year (and more) | No, not permitted to charge fees to parents or students |
| Admission | Selective admission policies | Open admission policy, accepts all students, often uses a lottery system |
| Curriculum | Typically follow traditional teaching methods | Greater flexibility in designing their own curriculum and teaching methods |
| Accountability | Not obligated to meet specific academic curriculum or performance standards | Held to high-performance standards, accountable to the government body that granted the charter, required to adhere to federal education laws and regulations |
| Governance | Often run by a single entity such as a church or educational organization | Independently operated, overseen by a board of directors responsible for managing the school's operations, accountable to the government body that granted the charter |
Funding

Charter schools and private schools differ significantly in terms of their funding sources. Charter schools receive funding from a variety of sources, including public institutions, non-government organizations, and private entities that align with the school’s philosophy. However, they are accountable to the government that grants them their charter.
In contrast, private schools use tuition, grants, donations, and endowments for funding.
Tuition Costs

There is a common misconception that charter schools require tuition fees from their students, but this is not the case. Charter schools are not permitted to charge any fees to parents or students, as all funding is provided by organizations that support the school’s mission and philosophy.
However, they may require students to pay fees for certain activities or programs, such as extracurricular activities or specialized courses. Additionally, some charter schools may require families to provide their own transportation or purchase uniforms.
In contrast, private schools typically charge tuition fees as their primary source of revenue, with the average cost being around $12,350 per year. Parents or guardians of students attending the school usually pay this cost.
Admission
Charter schools offer an open admission policy, meaning they accept all students regardless of their background. They often use a lottery system when they receive more applications than available spaces.
They must adhere to nondiscrimination laws and cannot selectively choose students based on academic performance, behavior, or other factors. According to the National Center for Education Statistics, private schools have a much lower diversity rate, with 72 percent of private schools having a population of 70 percent or more white students, compared to 30 percent of public charter schools.
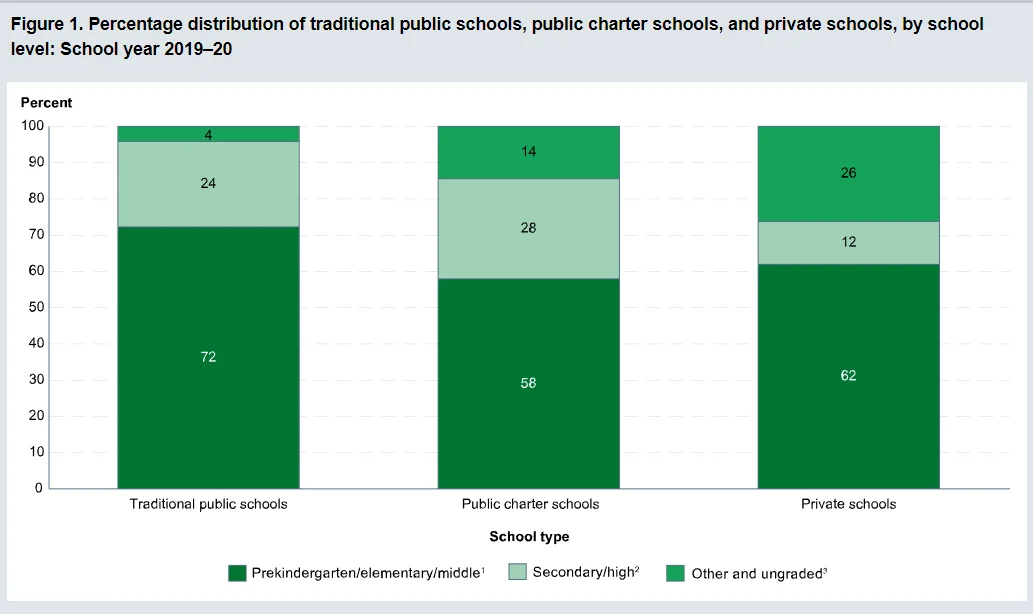
Source – NCSER
Private schools have selective admission policies and can choose which students to accept based on factors such as academic performance, behavior, and other criteria. While this approach may result in a higher-quality student body, it can also lead to less diverse student populations.
Curriculum:
Charter schools enjoy the advantage of greater flexibility in designing their own curriculum and teaching methods to meet the specific needs of their students. They are not bound by the constraints of standardized curriculums, which allows them to adapt and evolve their educational approach over time.
Private schools typically follow more traditional teaching methods and may rely heavily on standardized curriculums. While this approach can provide a solid foundation in core subjects, it may be less effective in catering to the diverse learning styles and needs of individual students.
Recommended for reading: IS PRIVATE SCHOOL WORTH IT?
Accountability:
Charter schools are held to high-performance standards and can revoke their charter if they fail to meet them. This level of accountability makes charter schools more answerable to the public than private schools, which are subject to different levels of oversight. Additionally, charter schools are required to adhere to federal education laws and regulations.
Private schools are not obligated to meet any specific academic curriculum or performance standards. While this can give them greater flexibility and autonomy in their educational approach, it also means that they are not held accountable to any specific academic benchmarks.
Governance:
Charter schools and private schools differ in their management and governance structures. Charter schools are typically independently operated and overseen by a board of directors responsible for managing the school’s operations, including hiring staff, setting policies, and developing curriculum.
The board is accountable to the government body that granted the charter, and the school’s operations must adhere to its terms.
Private schools, on the other hand, are often run by a single entity, such as a church or educational organization. This entity is responsible for the school’s management and operations. While private schools may have some level of autonomy in their decision-making processes, they are often more beholden to the interests of their owners or administrators.
Recommended for reading: BEST COMPUTER SCIENCE SCHOOLS IN TEXAS
Additional Factors:
| Additional Factors | Private Schools | Charter Schools |
|---|---|---|
| Special Education Services | Varies widely, some specialize in specific needs, others offer limited support | Not all offer specialized programs, but some cater to diverse learning styles |
| Teacher Certification | Not always required to hold state certification, but most do | Required to meet state certification standards like public schools |
| Cultural and Religious Influence | Many have religious affiliations, impacting curriculum and ethos | Legally secular, but individual schools may foster specific cultural values |
| Facilities and Resources | Often boast smaller class sizes, wider extracurricular options, and better facilities due to funding | Resources vary depending on the school, but may be similar to public schools |
Special Education Services:

Charter schools are mandated to provide special education services, ensuring that students with diverse learning needs receive appropriate support. This obligation is grounded in federal and state laws, emphasizing inclusivity. Research indicates that charter schools while making strides in this area, may sometimes face challenges due to resource constraints.
The National Center for Special Education Research (NCSER) emphasizes ongoing efforts to enhance special education services in charter schools, emphasizing the importance of equitable access to quality education for all students.
Teacher Certification:

Charter schools often have more flexibility in hiring teachers who may not hold traditional teaching certifications. The National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance (NCEE) notes that charter schools may employ individuals with expertise in specific fields or industries, contributing to a diverse teaching staff.
Conversely, private schools, bound by state regulations, generally require teachers to possess traditional teaching certifications, ensuring a standardized level of qualification. This distinction can impact the composition and diversity of the teaching workforce.
Recommended for reading: TOP 10 VETERANS DAY ACTIVITIES FOR MIDDLE SCHOOL STUDENTS
Cultural and Religious Influence:
Private schools, especially those affiliated with specific cultural or religious entities, may infuse their educational environment with distinctive cultural or religious influences. The Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD) suggests that this influence can shape the overall ethos and values of the institution.
Charter schools, being publicly funded and accountable, tend to be more secular in their approach, promoting a diverse and inclusive educational environment.
Facilities and Resources:

Image Source: latinamericanpost
Charter schools may need help in securing facilities and resources, often relying on their allocated funding. The Thomas B. Fordham Institute highlights that while some charter schools successfully leverage community partnerships and innovative resource allocation, others may need more funding.
Private schools, with tuition fees and additional financial support, may have more resources and potentially superior facilities, contributing to differences in the overall learning environment. However, it’s important to note that the quality of facilities and resources can vary widely within both charter and private school sectors, making it crucial to consider individual cases.
Recommended for reading: PRIVATE EDUCATION VS PUBLIC EDUCATION – KEY DIFFERENCES
Is a Charter School Better Than a Private School?
It is challenging to make a general statement about whether a charter school is better than a private school since the quality of education varies significantly between individual schools, regardless of their type. Choosing between a charter school and a private school depends on various factors, including the student’s learning needs, location, and personal preferences.
Ultimately, the decision between a charter school and a private school should be based on the student’s academic needs, extracurricular interests, and the family’s financial situation. Before making a decision, it’s essential to research and evaluate individual schools’ programs, faculty, and educational philosophies.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to choosing a charter or private school. The right school for your child depends on their academic and extracurricular needs and your family’s financial situation. You’ll need to do extensive research on each school’s program, faculty, and overall educational philosophy.
Moonpreneur is on a mission to educate and ignite the flames of entrepreneurship through our holistically created online STEM programs, which will help kids master the futuristic sciences such as Robotics, Game Development, App Development, Advanced Math, Math-Quiz to test your kids knowledge and much more!!
Register for a free 60-minute robotics workshop today!
















Can students be chosen from private schools using only academic standards?
Yes, students can be selected by private schools according to academic, religious, or other standards. Due to their public status, charter schools are required to use non-discriminatory admission practices, such as lottery admissions.